Cell Antigens & Receptors
The tumor or cell type-specific antigens are the targets for CAR-T cell recognition. The T cell surface-expressed antigens (receptors) are targets for immune-boosting or for anti-tumor boosting via target-over expression or suppression via knockdown or knockout.
Gentarget Provides the lentivirus products expressing an immune response gene, Cell surface antigens (CDs), immune checkpoint / Receptors. They can be used to generate, in your desired cell types.
1. Regulators on tumor cells and on T cells:
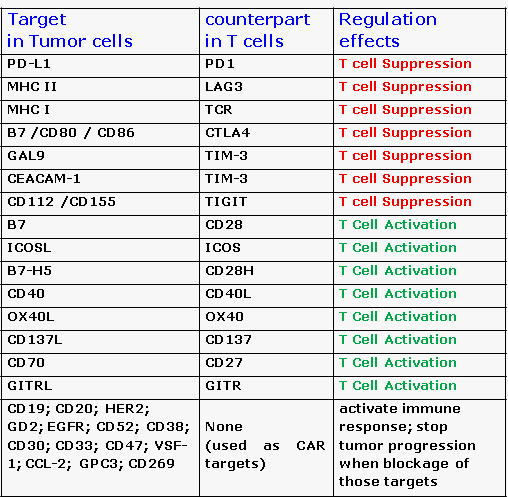
1) PD-L1 /PDL-2 and PD-1 (Programmed death-1):
PD-L1 and PD-L2, are expressed on the surface of tumor cells. Both bind for PD-1 that expressed in T cell surface which inhibits T-cell activity. Blocking the PD-1 signal pathway can stop tumor’s immune escape, activate T cell immunoreactions to cancers.
- CAT#: LVP1077; LVP1077-GP; LVP507
2) LAG3 (Lymphocyte-activation gene 3):
LAG-3 expressed on the surface of both activated cytotoxic T cells and regulatory T cells. Cancer cells active LAG-3 leads to T-cell exhaustion and eroding the ability of T cells to kill tumor cells. Inactivation of LAG-3 allowed T cells to regain cytotoxic function.
- CAT#: LVP1082
3) TCR (T-Cell Receptor):
The T-cell receptor (TCR) is a protein complex found on the surface of T cells, or T lymphocytes that is responsible for recognizing major histocompatibility complex (MHC I) molecules. Many TCRs recognize the same antigen peptide and many antigen peptides are recognized by the same TCR. TCR consists mainly, of an alpha (α) chain and a beta (β) chain (encoded by TRA and TRB, respectively). CAT#:
4) CTLA-4(Cytotoxic T-Lymphocyte-associated Antigen 4):
CTLA-4 /CD152 are expressed on the surface of T cells to maintain immune reaction balance. Tumor cells utilize the CTLA-4 pathway to suppress initiation of an immune response, resulting in decreased T-cell activation.
5) CD73:
CD73 is a cell-surface enzyme on regulatory T cells. Cancer cells express CD73 to reduce antitumor immunity. Tumor-derived CD73 is a contributor to immune escape in cancer. Inhibition of CD73 activity can stimulate T-cell activity.
- CAT#: LVP1099
6) IDO (Indoleamine-2,3-dioxygenase-1):
IDO is an intracellular enzyme for tryptophan metabolism which keeps T-cell immune responses under control. Tumor cells hijack this immunosuppressive process by up-regulate IDO activity. Blockade of IDO can restore cytotoxic T-cell function.
7) CD137 (4-1BB/ TNFRSF17 ):
It is expressed on both Natural Killer (NK) cells and T cells. Activation of CD137 signaling can stimulate both cytotoxic T-cell and NK-cell activity.
8) GITR(Glucocorticoid-induced TNFR-related protein):
GITR is an activating receptor on the surface of T cells and other immune cells. Once exposure to tumor antigen activates a T cell, the number of GITR receptors on its surface increases. Activation of GITR signaling can help enhance immunity through the activation of cytotoxic T cells. CAT#:
9) OX40 (CD134):
OX40 is an activating receptor expressed on the surface of activated cytotoxic T cells and regulatory T cells. On cytotoxic T cells, OX40 binds to its ligand (OX40L), resulting in stimulatory signals that promote T-cell reproduction, function, and survival, favorable to the antitumor immune response.
- CAT#: LVP1086;
10) SLAMF7 (Signaling Lymphocytic Activation Molecule Family member 7):
SLAMF7 (CD319)is expressed on the surface of virtually all Natural Killer (NK) cells and subsets of other immune cells. SLAMF7 activates NK cells, the rapid responders of the immune system and the body’s first line of defense against cancer, which also initiate the development of long-term immunity by T Cell memory.
- CAT#: LVP1094;
11) KIRs (Killer cell Immunoglobulin-like Receptors):
KIRs are expressed on the surface of Natural Killer (NK) cells and cytotoxic T cells. Normal cell expresses the ligand that inhibit KIRs that stop NK cells from killing normal cells. Tumor cells up-regulate the ligand for inhibitory KIRS in order to evade NK cell-mediated recognition and destruction. Blockade of inhibitory KIRs help restore NK cell-mediated immune activity.
- CAT#: LVP1081;
12) CSF1R(Colony-Stimulating Factor 1 Receptor):
CSF1R (CD115) is a cell-surface receptor expressed by macrophages and other cells. In some cancer, macrophages promote cancer survival. CSF1, the ligand for CSF1R, is a dominant regulator of macrophage differentiation and function. Cancer cell use upregulate CSF1 to target CSF1R on macrophages, supporting tumor growth. Blockade of CSF1R can deplete tumor-associated macrophages, thus improved T-cell responses.
13) CD28:
Depend on cell type, CD 28 promote proliferation and function of T cell, also it serves anti-inflammatory roles in regulatory T cell (Treg). CD28 is the only B7 (B7.1: CD80, B7.2: CD86) receptor constitutively expressed on naive T cells.
- CAT#: LVP1078;
14) CD40:
CD40 binds to CD154 (CD40L) on help T cells activate APC cell and enhance T cell response against Tumor.
- CAT#: LVP888;
15) CD80:
CD80 (B7.1) closely related to CD86 (B7-2), and often works in tandem, binding to the same receptors to prime T cells. CD80 binds to CD28 and CTLA-4 result in T and B-cell activation
- CAT#: LVP1080;
16) BCMA (CD269 / TNFRSF17), “B-cell maturation antigen” or “tumor necrosis factor receptor superfamily member 17”:
BCMA is a cell surface receptor of the TNF receptor superfamily, preferentially expressed in mature B lymphocytes. TNFRSF17 is implicated in leukemia, lymphomas, and multiple myeloma and used as a target of CAR-T therapy.
- CAT#: LVP713;
17) ICOS (CD278), Inducible T-cell co-stimulator:
ICOS is an immune checkpoint protein expressed on activated T cells. It promotes T-cell activation and proliferation;
- CAT#: LVP1079;
18) CD3ζ (CD3E / CD247), T-cell surface glycoprotein CD3 zeta chain:
It involved in forms the T-cell receptor-CD3 complex, coupling antigen recognition to several intracellular signal-transduction pathways. It activates the immune response.
- CAT#: LVP1163;
19) TGFB1, (Transforming growth factor beta 1):
TGFB1 is a secreted cytokine that performs many cellular functions. Regulatory T cells release TGF-β1 to inhibit the actions of other T cells and can inhibit the secretion and activity of many other cytokines. It also inhibits proliferation and stimulates apoptosis of B cells. TGF-β1 acts as a chemoattractant, directing an immune response to some pathogens.
- CAT#: LVP289;
2. Lentivirus express cell surface CD antigens (see below);
| Cat# | GENE Symbol |
| LVP066 | h FGFR1 (CD331) |
| LVP099 | h PROM1 (CD133) |
| LVP103 | h CXCR4 (CD184) |
| LVP1067 | h CD46 |
| LVP1073 | h CR2 (CD21) |
| LVP1076 | h PDCD1 (CD279, 6His) |
| LVP1077 | h CD274 (PDL1) (6His) |
| LVP1077-GP | h CD274 (PDL1) |
| LVP1078 | h CD28 (6His) |
| LVP1079 | h ICOS (CD278, 6His) |
| LVP1080 | h CD80 (6His) |
| LVP1082 | h LAG3 (CD223) |
| LVP1084 | h CD19 |
| LVP1084-GP | h CD19 (GFP-Puro) |
| LVP1085 | h CD22 (6His) |
| LVP1086 | h TNFRSF4 (CD134, 6His) |
| LVP1087 | h TNFRSF9 (CD137, 6His) |
| LVP1088 | h SDC1 (CD138, 6His) |
| LVP1089 | h MS4A1 (CD20, 6His) |
| LVP1090 | h IGF1R (CD221, 6His) |
| LVP1091 | h FCER2 (CD23, 6His) |
| LVP1092 | h CD27 (6His) |
| LVP1093 | h CD3g (6His) |
| LVP1094 | h SLAMF7 (CD319, 6His) |
| LVP1095 | h CD33 |
| LVP1096 | h CD38 (6His) |
| LVP1097 | h CD52 (6His) |
| LVP1098 | h CD70 (6His) |
| LVP1099 | h NT5E (CD73, 6His) |
| LVP1100 | h CD74 (6His) |
| LVP1101 | h CD86 |
| LVP1145 | h NRP1 (CD304) |
| LVP1148 | h MUC1 (CD227) |
| LVP1150 | h IL3RA (CD123) |
| LVP1151 | h CD8a |
| LVP1152 | h CD4 |
| LVP1153 | h CEACAM5 (CD66e) |
| LVP1157 | h TNFSF11 (CD254) |
| LVP1163 | h CD3E (CD247) |
| LVP1176 | h KDR (CD309) |
| LVP1181 | h FAS (CD95) |
| LVP1211 | h IL3RA (CD123) |
| LVP1312 | h CD50 (ICAM3) |
| LVP1313 | h CD16 (FCGR3A) |
| LVP1318 | h CD44 |
| LVP1320 | h CD1 |
| LVP1321 | h TFRC (CD71) |
| LVP1323 | h ITGB1 (CD29) |
| LVP1347 | h CD30 (TNFRSF8) |
| LVP1348 | h CD66 (CEACAM1) |
| LVP1349 | h CD26 (DPP4) |
| LVP1363 | m CD8 |
| LVP1365 | h CD111 (Nectin1) |
| LVP1368 | h CD64 (FCGR1A) |
| LVP1370 | m CD64 (Fcgr1) |
| LVP1377 | h KLRK1 (CD314) |
| LVP1395 | h HAVCR2 (CD366) (6His) |
| LVP1396 | h CD1D (6His) |
| LVP1418 | m CD274 / PDL1 (6His) |
| LVP162 | h FGFR2 (CD332) |
| LVP394 | h Flt3 (CD135) |
| LVP423 | h FASLG (CD178) |
| LVP476 | h CSF1R (CD115) |
| LVP504 | h ERBB2 (CD340) |
| LVP513 | h CCR6 (CD196) |
| LVP542 | h BSG (CD147) |
| LVP546 | m CD74 |
| LVP595 | h ICAM1 (CD54) |
| LVP607 | h INSR (CD220) |
| LVP609 | h TNFSF10 (CD253) |
| LVP611 | h MAOB (CD253) |
| LVP613 | h IL6R (CD126) |
| LVP625 | h IL2RA (CD25) |
| LVP631 | m Ms4a1 (CD20) |
| LVP641 | h CD59 |
| LVP643 | r CD59 |
| LVP647 | h MME (CD10) |
| LVP713 | h TNFRSF17 (CD269) |
| LVP718 | h CD14 |
| LVP719 | h CCR1 (CD191) |
| LVP722 | h S1PR1 (CD363) |
| LVP733 | h IFNGR1 (CD119) |
| LVP735 | h ITGA1 (CD49a) |
| LVP743 | h TLR1 (CD281) |
| LVP744 | h TLR2 (CD282) |
| LVP745 | h TLR3 (CD283) |
| LVP746 | h TLR4 (CD284) |
| LVP750 | h TLR6 (CD286) |
| LVP753 | h TLR8 (CD288) |
| LVP754 | h TLR9 (CD289) |
| LVP755 | h TLR10 (CD290) |
| LVP757 | h CD9 |
| LVP758 | h CD81 |
| LVP765 | h IL10RA (CD210) |
| LVP783 | h FGFR3 (CD333) |
| LVP826 | m CD40LG (CD154) |
| LVP843 | h PDGFRB (CD140b) |
| LVP877 | h CTLA4 (CD152) |
| LVP878 | h CD40LG |
| LVP879 | h TNFSF14 (CD258) |
| LVP888 | h CD40 |
| LVP916 | m CTAGA1 (CD152) |
| LVP918 | h CD47 |
| LVP922 | h TNFRSF1B (CD120b) |
| LVP935 | h FcRL3 (CD307c) |
3. Lentivirus express Cytokines (see below);
4. Immune checkpoint / Receptors (see below);