Introduction
RNA polymerase II is the main promoter category driving expression of thousands of genes, and its transcriptional mechanisms have been widely investigated. It involves many transcription factors and a combinatorial array of cis-regulatory DNA elements. Two transcription initiation complexes have been well characterized: the Core promoter and the Co-regulators.
The core promoter is defined as the minimal stretch of contiguous DNA sequence that is sufficient to direct accurate initiation of transcription by RNA polymerase II. The co-regulators are other cis-acting DNA sequences including the proximal promoter, enhancers, silencers, and Boundary / insulator elements.
The Core promoter extends either upstream or downstream for ~ 37bp at the transcription initiation site, which include BBE (TFIIB recognition element), the TATA box, Inr (initiator), and DPE (downstream promoter element) (see schematic map below, Jennifer 2002).
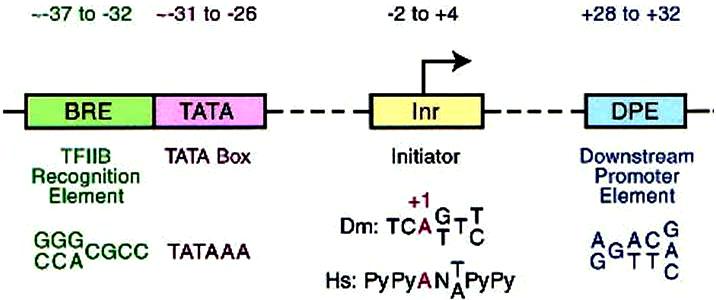
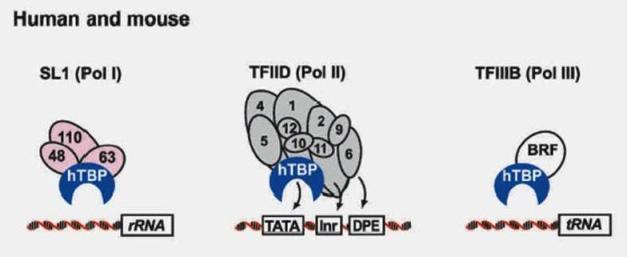
Co-regulators: The proximal promoter is the region in the immediate vicinity of the transcription start site (roughly from -250 to +250 nt). The binding sites for enhancers and repressors of transcription can be located many kbp from the transcription start site and act either to activate or to repress transcription.
What is the enhanced super CMV promoter?
GenTarget engineered the wild-type CMV promoter regions after aligned varieties of poly II promoters, and made a series of mutations inside the upstream enhancer, Inr and DPE. We screened the re-engineered CMV promoter’s efficiency by investigating the following aspects:
- The performance of the enhancer in the upstream regulator region
- The necessity of the TATA box
- The amount of DPE needed to increase transcription efficiency
- The effect of spacer length between the transcription initiation site and the translation initiation site
- The effect of an Intron in the downstream regulatory element
Our proprietary suCMV promoter has 6 mutations in its enhancer region, 3 mutations inside the core promoter region, the optimized spacer distance between transcription and translation initiation sites, and an artificial intron at downstream of transcription site. Dependent upon cell types, this suCMV promoter demonstrated 4 to 6 folds higher translation efficiency than that in pCDNA3.1, and 2 to 3 fold higher than that in pcDNA3.3 (see Fig 3 below).
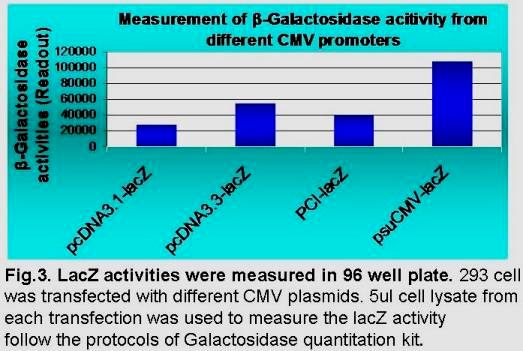
The engineered super CMV promoter with the strongest transcription/translation efficiency was selected and integrated into our lentiviral vectors and Eco-PCR cloning expression vectors.
Depending upon cell type, this suCMV promoter demonstrates 4-6 fold higher translation efficiency than pCDNA3.1, and 2-3 fold higher than pcDNA3.3 (see Fig 3 below).
References:
- Jennifer E.F. Butler1 and James T. Kadonaga. GENES & DEVELOPMENT 16:2583-2592, 2002.
- Tamar JG, et al. Rational design of super core promoter that enhances gene expression. NATURE METHOD. V3(11):917-922, 2006.
- Nikolov, D., H. et al. Crystal structure of a TFIIBTBP-TATA-element ternary complex. Nature 377: 119-128, 1995.
- MICHAEL HAMPSEY MICROBIOLOGY AND MOLECULAR BIOLOGY REVIEWS, 1998, p. 465-503